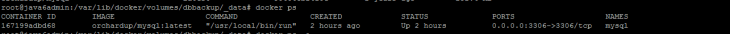What is Docker ?
https://www.docker.com
Docker is a tool designed to make it easier to create, deploy, and run applications by using containers. Containers allow a developer to package up an application with all of the parts it needs, such as libraries and other dependencies, and ship it all out as one package. By doing so, thanks to the container, the developer can rest assured that the application will run on any other Linux machine regardless of any customized settings that machine might have that could differ from the machine used for writing and testing the code.
In a way, Docker is a bit like a virtual machine. But unlike a virtual machine, rather than creating a whole virtual operating system, Docker allows applications to use the same Linux kernel as the system that they’re running on and only requires applications be shipped with things not already running on the host computer. This gives a significant performance boost and reduces the size of the application.
And importantly, Docker is open source. This means that anyone can contribute to Docker and extend it to meet their own needs if they need additional features that aren’t available out of the box.
Docker Architecture
Docker consist with containers and images, We can run images on different containers. for more architectural information please refer this link.

The Docker daemon
The Docker daemon runs on a host machine. The user uses the Docker client to interact with the daemon.
The Docker client
The Docker client, in the form of the docker binary, is the primary user interface to Docker. It accepts commands and configuration flags from the user and communicates with a Docker daemon. One client can even communicate with multiple unrelated daemons.
Inside Docker
To understand Docker’s internals, you need to know about images, registries, and containers.
Docker images
A Docker image is a read-only template with instructions for creating a Docker container. For example, an image might contain an Ubuntu operating system with Apache web server and your web application installed. You can build or update images from scratch or download and use images created by others. An image may be based on, or may extend, one or more other images. A docker image is described in text file called a Dockerfile, which has a simple, well-defined syntax. For more details about images, see How does a Docker image work?.
Docker images are the build component of Docker.
Docker containers
A Docker container is a runnable instance of a Docker image. You can run, start, stop, move, or delete a container using Docker API or CLI commands. When you run a container, you can provide configuration metadata such as networking information or environment variables. Each container is an isolated and secure application platform, but can be given access to resources running in a different host or container, as well as persistent storage or databases. For more details about containers, see How does a container work?.
Docker containers are the run component of Docker.
Docker registries
A docker registry is a library of images. A registry can be public or private, and can be on the same server as the Docker daemon or Docker client, or on a totally separate server. For more details about registries, see How does a Docker registry work?
Docker registries are the distribution component of Docker.
Docker services
A Docker service allows a swarm of Docker nodes to work together, running a defined number of instances of a replica task, which is itself a Docker image. You can specify the number of concurrent replica tasks to run, and the swarm manager ensures that the load is spread evenly across the worker nodes. To the consumer, the Docker service appears to be a single application. Docker Engine supports swarm mode in Docker 1.12 and higher.
Docker services are the scalability component of Docker.
Install Docker
Install on Windows – https://docs.docker.com/engine/installation/windows/
Install on Ubuntu – https://docs.docker.com/engine/installation/linux/ubuntulinux/
Note : Enable virtualization on your laptop/computer before continue docker. You can enable this option by accessing the boot menu of your computer.
How to use Docker in our projects?
Eg : Host ui-web / service-web / mysql (host two war files which is depends on one another with mysql server using docker engine. ui-web is the angular app, service-web is the spring boot application, mysql is the database server. angular app calls services on spring boot application and spring boot application access mysql database server)
Step 01 – Add Dockerfile to the angular application/ui-web
Add below code list in a file. File name should be exactly Dockerfile (no extension).
FROM jboss/wildfly
ADD ui-web.war /opt/jboss/wildfly/standalone/deployments/
Step 02 – Add Dockerfile to the Spring boot application/service-web
Add below code list in a file. File name should be exactly Dockerfile (no extension).
FROM jboss/wildfly
ADD service-web.war /opt/jboss/wildfly/standalone/deployments/
Step 03 – Create a yml file
Add below code list in a file. File name could be differ. extension shoule be .yml
db:
image: orchardup/mysql
environment:
MYSQL_USER: <db username>
MYSQL_PASSWORD: <db password>
MYSQL_DATABASE: <db name>
ports:
- "3306"
services-web:
build: <path to the docker file eg: service/. (service is a directory, dot represent docker file)>
links:
- db:mysql #(since service web access mysql server this is the link to access mysql image)
ports:
- "8080"
ui-web:
build: ui-web/.
links:
- services-web:services-web #(since ui-web access service-web controller, this is the link)
ports:
- "8080"
Step 04 – Execute yaml file
<yaml file name> up
Now we have created all the images we want. You can list down created images using below command.
docker images
Result :

Step 05 – Start mysql Server
docker run -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=admin -p 3306:3306 --name mysql -d orchardup/mysql:latest
-e –> Set an environment variable (can be used multiple times)
-name –> Assign a name to the container
-d –> detache mode enable to run process background
orchardum/mysql –> image name
:latest –> tag name
Note: you can use any type of mysql client to access the database server to create databases or run scripts.
For more information, please refer this link.
Step 06 – Start service-web/spring boot application
docker run -p 8080:8080 --link mysql:mysql <service web image name>
Note : link should be set to mysql container as above.
Step 07 – Start ui-web/Angular application
docker run -p 8080:8080 --link service-web:service-web <ui web image name>
Note : link should be set to mysql container as above.
Note: After step 07, you may be able to access the system as you expected.
Note:
You can list your exising containers using below command.
docker ps -a
Result :

You can list your running container using below command.
docker ps
Result:
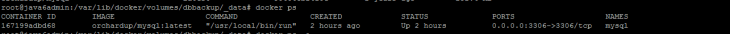
Using Volume with Docker
Docker container is volatile, data will be deleted if container is deleted. So we need volume to store container data.
A data volume is a specially-designated directory within one or more containers that bypasses the Union File System. Data volumes provide several useful features for persistent or shared data:
Volumes are initialized when a container is created. If the container’s base image contains data at the specified mount point, that existing data is copied into the new volume upon volume initialization. (Note that this does not apply when mounting a host directory.)
Data volumes can be shared and reused among containers.
Changes to a data volume are made directly.
Changes to a data volume will not be included when you update an image.
Data volumes persist even if the container itself is deleted.
Data volumes are designed to persist data, independent of the container’s life cycle. Docker therefore never automatically deletes volumes when you remove a container, nor will it “garbage collect” volumes that are no longer referenced by a container.
For more information, please refer this link.
Create Volume for Container Mysql
Use below command to create a volume for mysql container,
docker run -d -p 3306:3306 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=admin -v <volume name>:<location for the backup> --name mysql orchardup/mysql:latest
eg:
docker run -d -p 3306:3306 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=admin -v dbbackup:/var/lib/mysql --name mysql orchardup/mysql:latest
Note: when you create a volume, even though you deleted the container; you can create another container using an existing volume using above command. Then the container will be injected from the existing volume(stored data in the volume, in this scenario mysql database backup).
You can list your existing volumes under /var/lib/docker/volumes
Other Useful Commands for Docker
To delete containers,
docker rm -f <comntainer name>
To delete Images,
docker rmi -f <image name>
Note: You can use -f to force delete the container or image.











 Note : You can find the location url in this link.
Note : You can find the location url in this link.